What are WiFi
WiFi
and way does WiFi work?
many people are using WiFi technology and many of them don't answer these
questions.
WiFi - wireless local area network refers
to the wireless networks which use the 802.11 standards developed by the IEEE. WiFi
or Wi-Fi may be a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. WiFi Alliance tests
equipment of varied WiFi vendors and issues a certification. If the wireless
product is WiFi certified there's an assurance it acts consistent with the
802.11 standards.
There is also a widely used name for WiFi
networks and this is often WLAN. WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network, or Wireless
LAN is a local network-supported WiFi technology. So now once you know what's
WiFi lets determine how WiFi works.
WLAN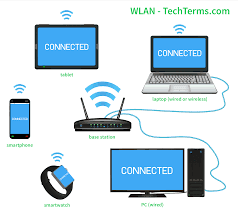
WLAN
uses different IEEE standards for data
transfer:
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
802.11a works on the frequency of 5 GHz.
Most of the wireless signals use the two .4GHz band, so there's much greater
possibility for decreasing the strength of the signal, because interference
with other signals that work on an equivalent frequency. Speed employed by
this standard is 54Mbps and it's almost 5 times greater than the speed of 802.11b
standard.
802.11b works on the frequency of two.4
GHz and with a maximum speed of 11 Mbps. This frequency of two.4 GHz is an unregulated frequency and therefore the providers don't need to pay the license
for it. The home in the indoor environment is about 35 meters (117 feet), and
100 meters (333 feet) in the outdoor environment.
802.11g works on the frequency of two.4
GHz, with a maximum speed of 54Mbps. Hardware is compatible with 802.11b
hardware.
What is WiFi 802.11n? it's still not
standard, it's an amendment. this is often a reason it operates on both frequency
bands 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Most of the vendors use a 2.4 GHz frequency. The
equipment performing on 802.11n is backward compatible with old standards. this
suggests that 2.4 GHz 802.11n is compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g.
Speed is typically 150Mbps, but a number of wireless routers could work even on 300 Mbps. The range is 6 times father
comparing to 802.11g.
Since it's still not standardized, of these
values of speed and range you ought to deem granted. If you're buying new
wireless equipment, it's good to require the one which supports n. But I would
not recommend changing the 802.11g wireless router and cards which are already
working fine with the most recent n amendment. There might be quite a difference
between actual results and therefore the speeds and ranges that vendors are
mentioning.
What is WiFi equipment?
As I even have already mentioned here, WiFi
uses the WLAN standard for a connection between the wireless access points or
broadband wireless routers and wireless clients or computers with Wireless
internet card.
WLAN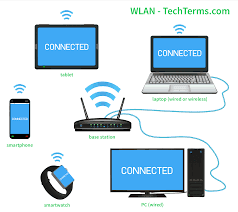
WLAN
uses nine WLAN network services for the transfer of packets and management operations. WiFi technology uses WLAN
formation and WLAN infrastructure.
A broadband wireless router may be a wireless
access point that has routing functionalities which has a broadband connection. A broadband connection is provided by fiber optics, DSL, Ethernet, or cable modem.
Every wireless broadband router may be a Wireless access point (connects
wireless devices like computers and PDA-s to a wired network) with broadband
access and a router (a device that forward packets between computer networks)
at an equivalent time.
What is a WiFi card? It connects devices to
the wireless LAN network or the WiFi network. On the web, you'll find the choice
names WiFi card and wireless network card. Wireless network cards support one
or more 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n WiFi standards.



No comments:
Post a Comment